
Human Skin Anatomy, Labeled Version Stock Vector Illustration of
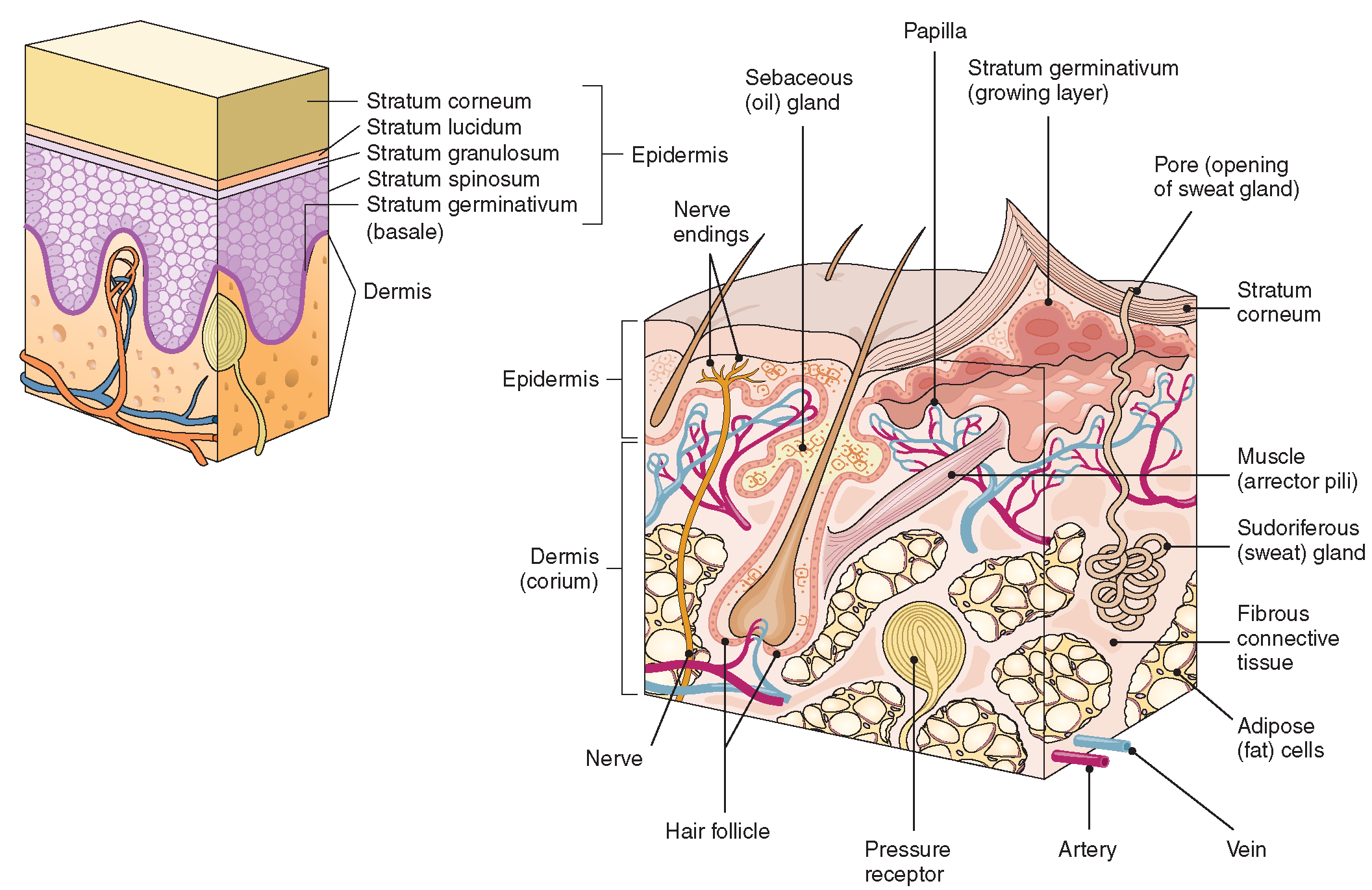
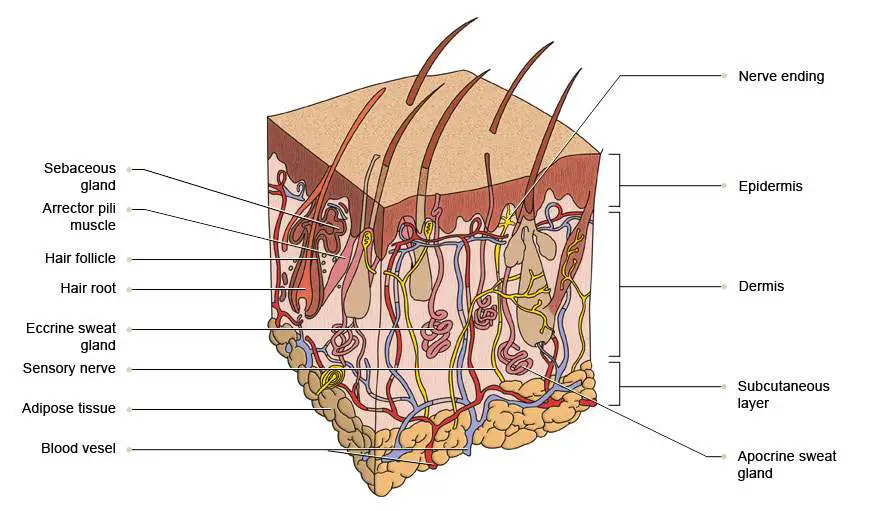
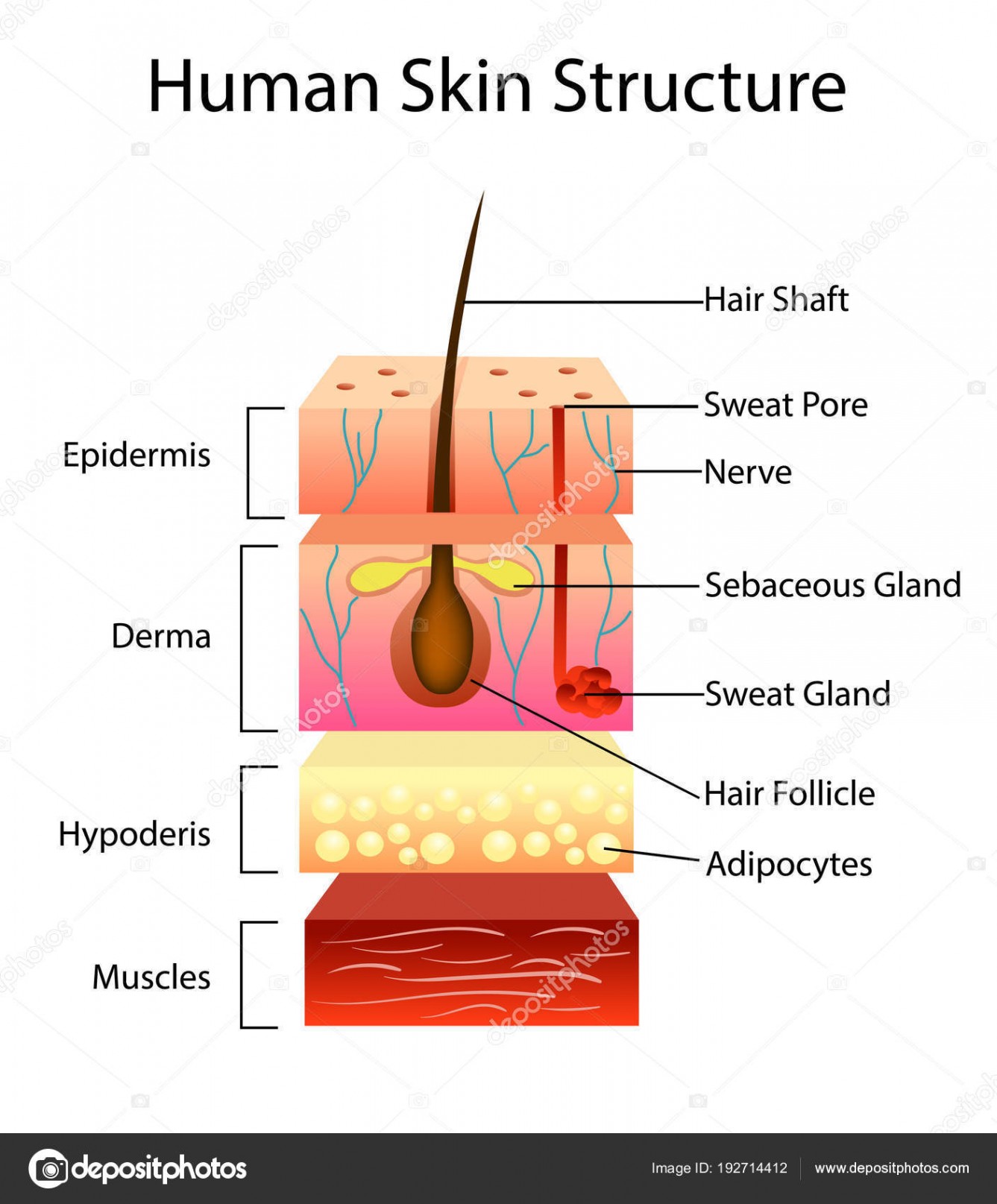
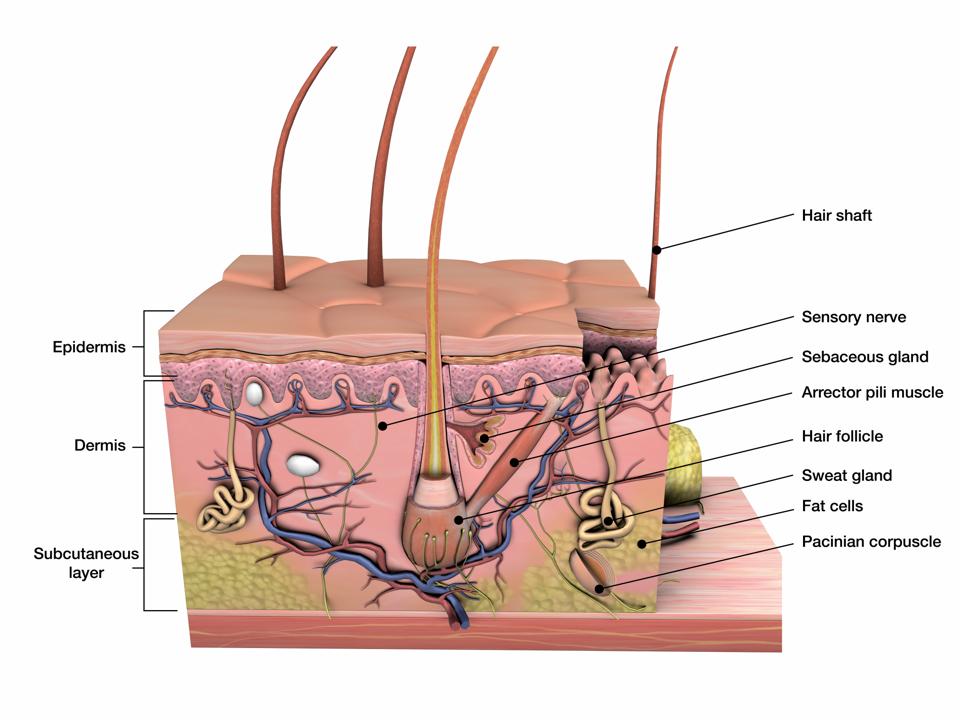
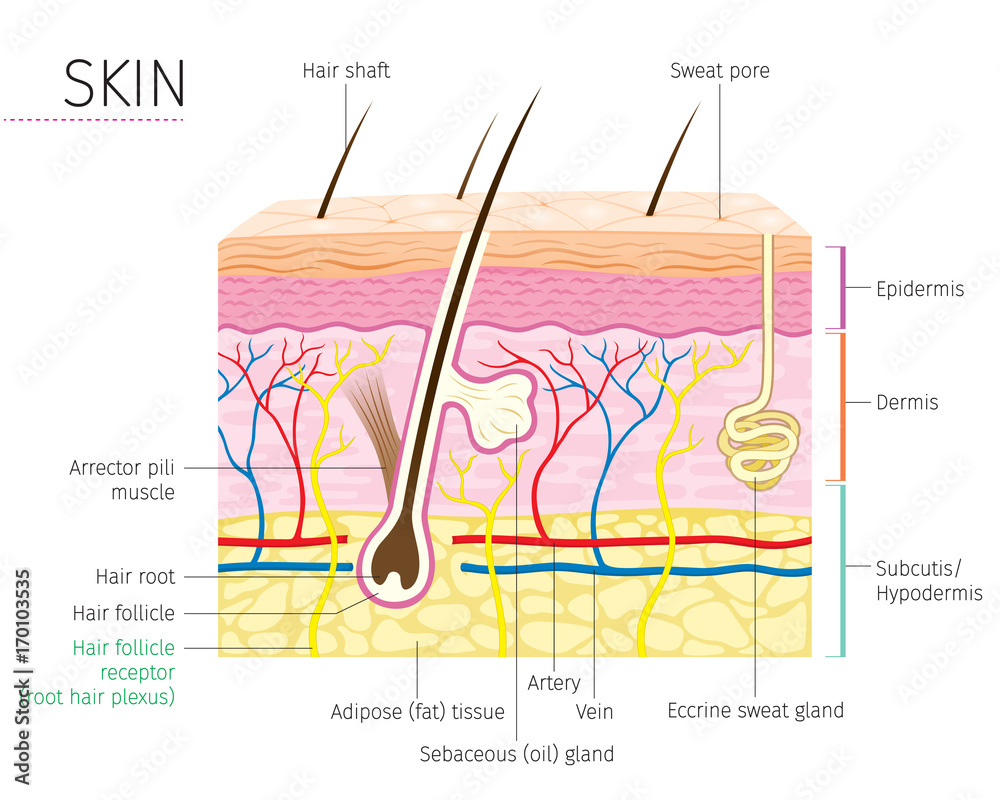
The skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures. Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which is composed mainly of loose connective and fatty tissues.
The Integumentary System (Structure and Function) (Nursing) Part 1
Functions of the skin. Some of the many roles of skin include: Protecting against pathogens. Langerhans cells in the skin are part of the immune system. Storing lipids (fats) and water. Creating.
Skin diagram labeled
Overview The three layers of skin on top of muscle tissue. What is the skin? The skin is the body's largest organ, made of water, protein, fats and minerals. Your skin protects your body from germs and regulates body temperature. Nerves in the skin help you feel sensations like hot and cold.

Diagram of human skin layers Charlotte Desire
Figure 5.1.1 - Layers of Skin: The skin is composed of two main layers: the epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures.
Skin diagram labeled
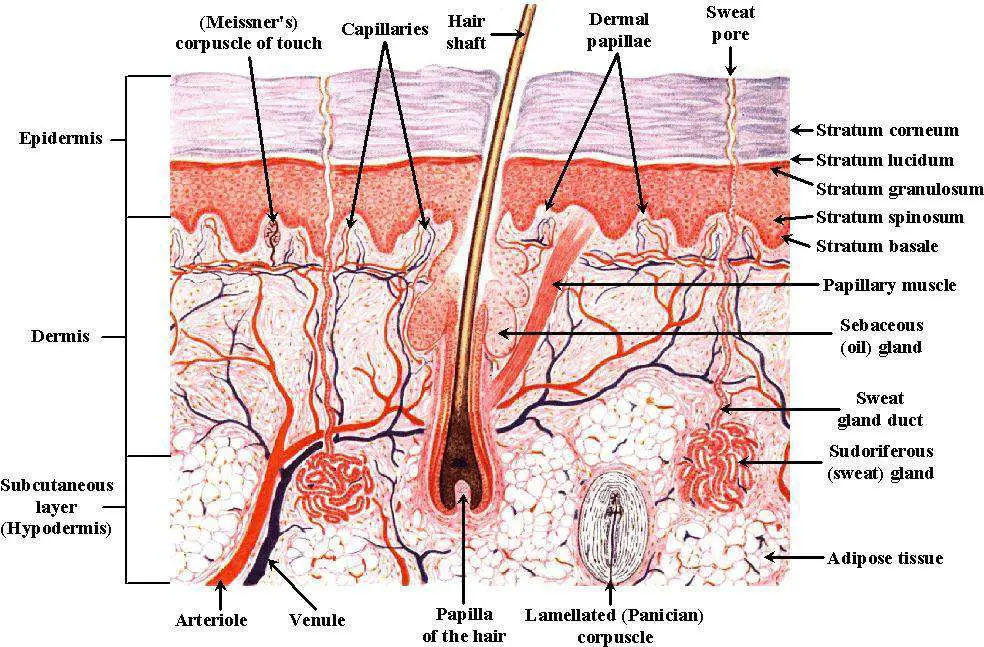
The skin consists of three layers of tissue: the epidermis, an outermost layer that contains the primary protective structure, the stratum corneum; the dermis, a fibrous layer that supports and strengthens the epidermis; and the subcutis, a subcutaneous layer of fat beneath the dermis that supplies nutrients to the other two layers and that cush.

Understanding How Your Skin Works School of Natural Skincare
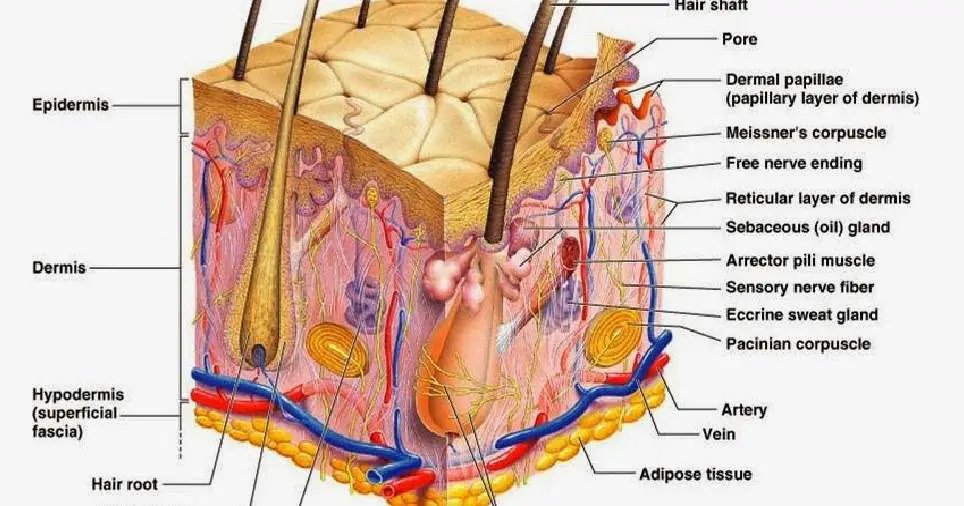
Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous fat layer (hypodermis) Each layer has certain functions. Epidermis The epidermis is the thin outer layer of the skin. It consists of 2 primary types of cells: Keratinocytes. Keratinocytes comprise about 90% of the epidermis and are responsible for its structure and barrier functions. Melanocytes.

Skin Model Labeled Bing Images Skin anatomy, Physiology, Anatomy
This article will discuss the anatomy of the skin, including its structure, function, embryology, blood, lymphatic, and nerve supply, surgical, and clinical significance. [1] [2]

Structure and composition of the skin [5]. Download Scientific Diagram
Stratum basale, also known as stratum germinativum, is the deepest layer, separated from the dermis by the basement membrane (basal lamina) and attached to the basement membrane by hemidesmosomes. The cells found in this layer are cuboidal to columnar mitotically active stem cells that are constantly producing keratinocytes.

Skin anatomy. Human normal skin Background Graphics Creative Market
Interactive Link The skin consists of two main layers and a closely associated layer. View this animation to learn more about layers of the skin. What are the basic functions of each of these layers? The Epidermis The epidermis is composed of keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium.
Skin diagram labeled
Stratum Corneum The stratum corneum is the top layer of the epidermis. Its jobs are to: Helps your skin retain moisture Keep unwanted substances out of your body It is made of dead, flattened cells called keratinocytes that are shed approximately every two weeks.

Skin Structure Diagram Best Picture Collection
Layers of Skin: How Many, Diagram, Model, Anatomy, In Order The Layers of Your Skin Your skin includes three layers known as epidermis, dermis, and fat. Some health issues, such as.
Labelled Pictures Of Human Skin / skin diagram /medical/anatomy/skin
Explore the skin diagram and how many layers of skin humans have. Learn about skin tissue, see how thick skin is, and identify the seven layers of human skin. Updated: 11/21/2023

human skin cells labeled Google Search Subcutaneous tissue, Skin
The skin is by far the largest organ of the human body, weighing about 10 pounds (4.5 kg) and measuring about 20 square feet (2 square meters) in surface area. It forms the outer covering for the entire body and protects the internal tissues from the external environment. The skin consists of two distinct layers: the epidermis and the dermis.
Rep. Ayanna Pressley Reveals Alopecia, What Is This Condition
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system.The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue guarding muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs.Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear hairless.
Skin Diagram Labeled
The skin is the body's largest organ. It covers the entire body. It serves as a protective shield against heat, light, injury, and infection. The skin also: Regulates body temperature. Stores water and fat. Is a sensory organ. Prevents water loss. Prevents entry of bacteria.
Skin diagram to label Labelled diagram
Biology Important Diagrams Skin Diagram Skin Diagram The largest organ in the human body is the skin, covering a total area of about 1.8 square meters. The skin is tasked with protecting our body from external elements as well as microbes. Interesting Note: